Understanding Inflation and Its Impact
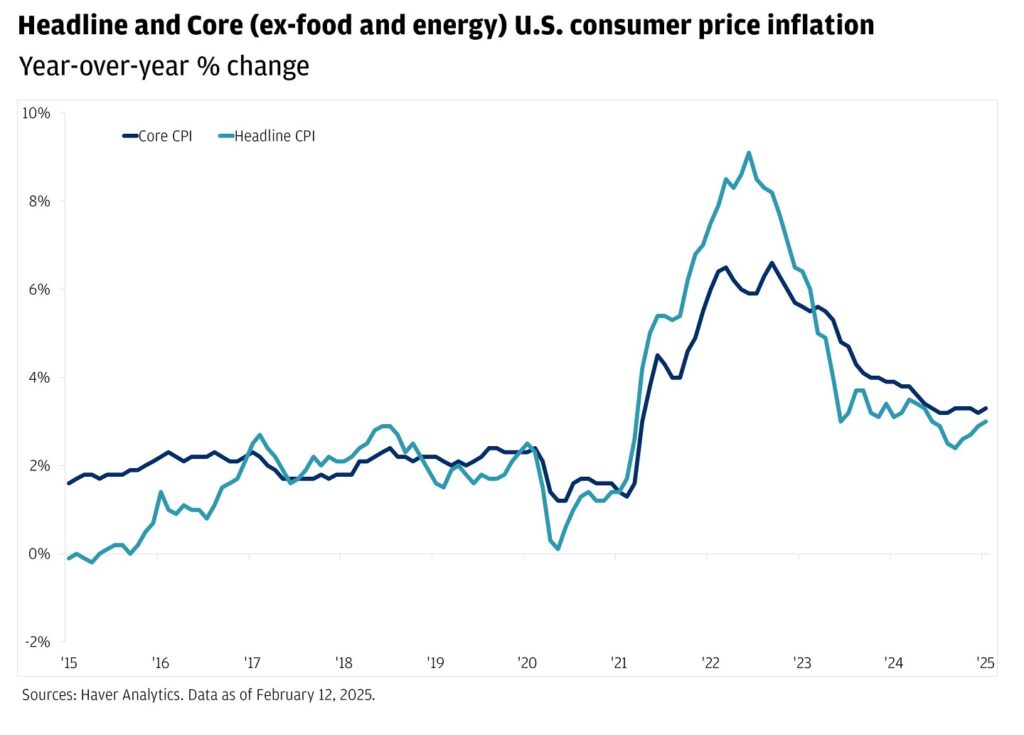
Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. When inflation is high, consumers find that their money doesn’t stretch as far as it used to. The latest data on US inflation rates has raised concerns among economists and consumers alike, as it reflects the ongoing challenges in the economy. With the Consumer Price Index (CPI) being a primary indicator of inflation, recent reports show fluctuations that can significantly affect household budgets.
Current Inflation Trends
As of the latest reports, inflation rates in the US have shown signs of both progression and stagnation. After reaching a peak in the previous year, there have been fluctuations in the monthly CPI readings. This means while some sectors are experiencing price stabilization, others continue to see increases. For example, essential goods like food and energy have seen more significant price hikes, impacting the daily lives of consumers who rely on these necessities.
What the Data Means for Consumers
For consumers, rising inflation translates into higher costs of living. With prices increasing in essential categories, families must adjust their budgets accordingly. Households may need to prioritize spending, cutting back on discretionary items to accommodate higher essential costs. This shift can lead to reduced consumer confidence, as families feel the pinch of tighter budgets. Furthermore, if inflation persists, it could lead to changes in consumer behavior, such as delaying purchases or seeking cheaper alternatives.
Interest Rates and Borrowing Costs
In response to rising inflation, the Federal Reserve may consider adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates can help curb inflation but can also make borrowing more expensive. For consumers, this means that loans for homes, cars, and credit cards may become costlier. As borrowing costs rise, potential homebuyers might delay purchases, leading to a slowdown in the housing market. Additionally, higher interest rates can affect existing loans, causing monthly payments to increase for those with variable-rate debts.
Long-Term Outlook and Consumer Strategies
While current inflation rates present immediate challenges, the long-term outlook remains uncertain. Economic experts advise consumers to stay informed about inflation trends and adjust their financial strategies accordingly. This may include building an emergency fund, investing wisely, and considering fixed-rate loans to mitigate the impact of rising interest rates. Being proactive can help consumers better navigate the challenges posed by inflation and maintain their financial stability.
Conclusion
The latest data on US inflation rates underscores the complex economic landscape facing consumers today. As essential goods and services become more expensive, households must adapt their spending habits and financial strategies. By staying informed and proactive, consumers can better manage the effects of inflation and work towards financial resilience in an ever-changing economic environment.