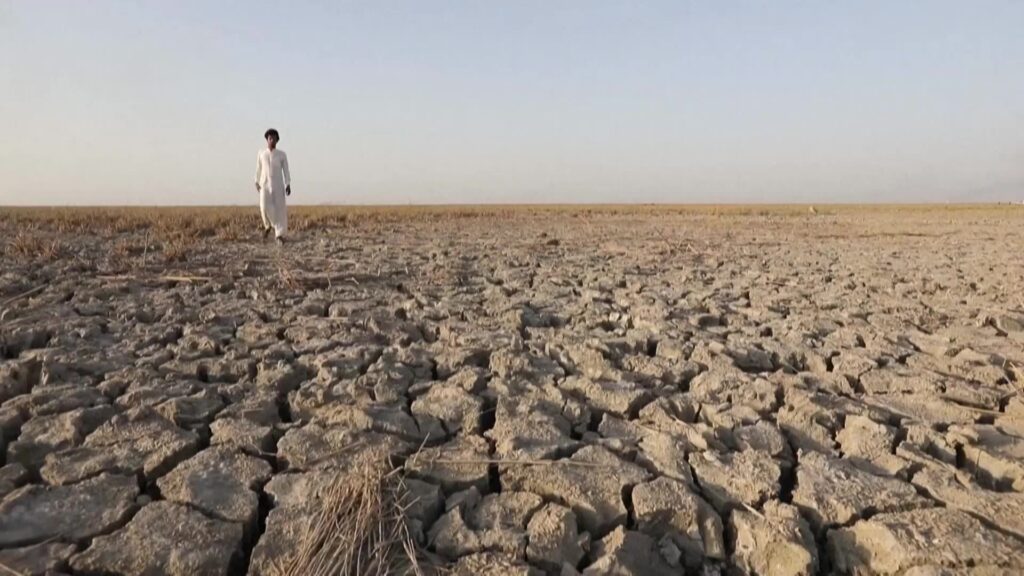
Water scarcity is an increasingly pressing issue in the Middle East, a region characterized by its arid climate and limited freshwater resources. As populations grow and economies develop, the demand for water is rising at an alarming rate. The Middle East, often referred to as one of the most water-scarce regions in the world, faces significant challenges in managing its water resources effectively. This situation is exacerbated by climate change, political conflicts, and poor water management practices.
Factors Contributing to Water Scarcity
Several factors contribute to the acute water scarcity in the Middle East. The region is predominantly desert, with only a few river systems and aquifers providing the majority of its water supply. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Kuwait rely heavily on desalination plants to meet their water needs, a process that is energy-intensive and expensive. Additionally, the growing population and urbanization put immense pressure on these limited water resources.
Climate change further complicates the situation, leading to unpredictable rainfall patterns and prolonged droughts. Many countries in the region have experienced significant reductions in precipitation over the past few decades, diminishing the availability of surface water. Furthermore, poor water management practices, including over-extraction of groundwater and inefficient irrigation techniques, have exacerbated the problem.
The Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
Agriculture is a critical sector in the Middle East, providing livelihoods for millions and contributing to the food supply. However, water scarcity poses a severe threat to agricultural productivity. Many farmers rely on irrigation, which is becoming increasingly unsustainable due to dwindling water resources. As the competition for water intensifies, agricultural yields are likely to decline, leading to food insecurity and higher prices.
In response to water scarcity, some countries are investing in modern irrigation technologies and drought-resistant crops. However, the transition is slow, and many smallholder farmers lack the resources to adapt. This situation puts additional strain on the region’s food systems, making it imperative for governments to prioritize sustainable water management practices.
Political and Social Dimensions of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity in the Middle East is not solely an environmental issue; it is also deeply intertwined with political and social dynamics. Disputes over shared water resources often lead to tensions between neighboring countries. For example, the Nile River, shared by several nations, has been a source of conflict, particularly between Egypt and Ethiopia over the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam.
Socially, water scarcity can exacerbate existing inequalities and lead to unrest. Marginalized communities often bear the brunt of water shortages, which can lead to protests and social instability. Governments must navigate these complex social dynamics while implementing policies aimed at equitable water distribution.
Strategies for Mitigating Water Scarcity
To address the growing concern of water scarcity, a multi-faceted approach is essential. Countries in the Middle East are increasingly exploring innovative solutions, such as investing in advanced desalination technologies, rainwater harvesting, and wastewater recycling. These strategies can help augment water supplies and reduce reliance on traditional sources.
International cooperation is also crucial in managing transboundary water resources. Collaborative agreements between countries can foster better water management practices and mitigate potential conflicts. Additionally, public awareness campaigns are necessary to promote water conservation and responsible usage among citizens.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Water scarcity in the Middle East is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires urgent attention. As the region grapples with the challenges posed by climate change, population growth, and political tensions, it is imperative for governments, communities, and international organizations to work together to find sustainable solutions. By prioritizing efficient water management practices and fostering cooperation, the Middle East can begin to address its water scarcity crisis and secure a more sustainable future for its inhabitants.